As the global pandemic spread, countries worldwide had to go into lockdown to keep the virus from spreading. Many companies were left with no other option than to shift to online work.
Working remotely has its benefits — employees spend less time commuting and are more productive. But there are also major security challenges.
Employees who don’t take the necessary precautions can compromise sensitive information and leave their company vulnerable to cyber attacks.
This article will cover essential cybersecurity practices for remote teams to follow that can safeguard your company against cyberattacks.
1. Establish a Cybersecurity Policy
IT teams generally handle cybersecurity in the office. But maintaining data security becomes more challenging with a distributed workforce.
According to Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report, 85% of data breaches occur because of human error. An estimated 36% involved phishing — an attack where an email or message appears legitimate but tricks victims into revealing personal information.
So how can you protect your organization against such attacks?
Start by establishing a cybersecurity policy. This document outlines the rules and security measures that all employees must follow.
Cybersecurity policies should cover the following:
- Acceptable use of email
- Connecting to public Wi-Fi networks
- Creating strong passwords
- Enabling two-factor authentication
- Handling customer information
- Using removable media
Outline the security protocols that you expect employees to comply with. For example, if remote workers need to access client information, they must understand the steps they need to take first.
Require all employees to review and sign the cybersecurity policy, whether they’re working remotely or not. Be sure to periodically revisit the policy and update it when necessary.
2. Make Use of VPNs
Part of the appeal of working remotely is the flexibility it provides. Employees can get their work done at home or go to their local cafe for a change of scenery.
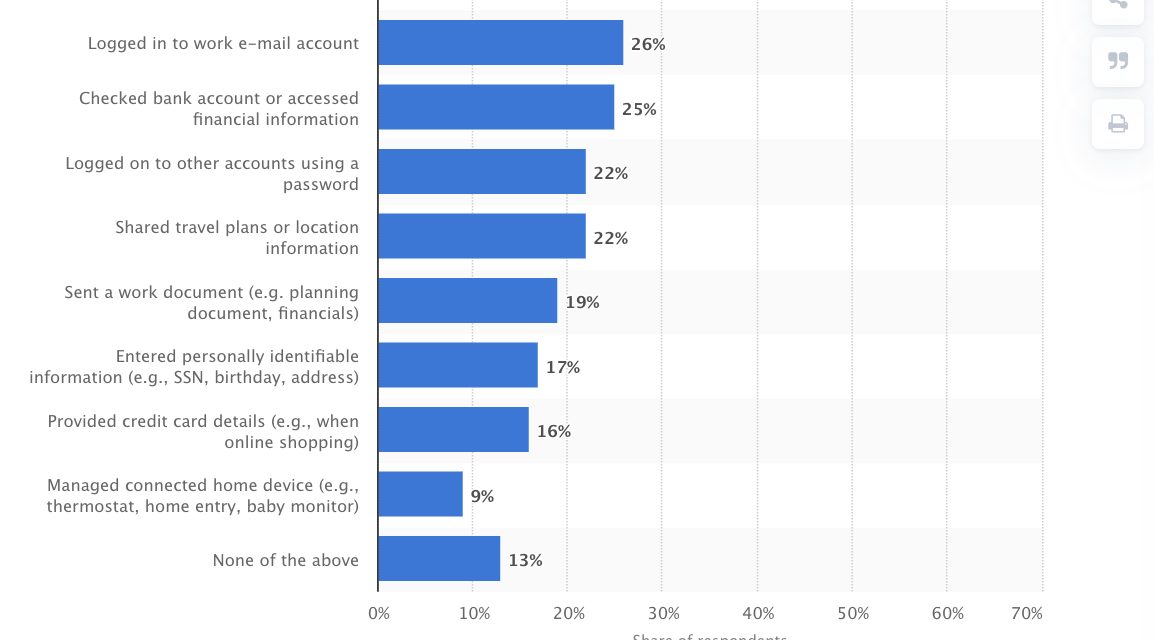
But when employees connect to a public Wi-Fi network, there’s a major security risk. If the connection point isn’t secure, hackers can intercept data that passes through the network and steal confidential information.
Despite these risks, 26% of internet users have logged in to a work email account, and 19% have sent a work document over public Wi-Fi.
One solution is to make use of virtual private networks or VPNs — a service that can establish a secure and encrypted tunnel between a user’s device and the internet.
The level of encryption that premium VPN providers like ExpressVPN provide makes it virtually impossible for anyone to track your online activities or view your data.
Make sure that employees leave their VPN on at all times to ensure that connections are always secure.
3. Use Strong and Secure Passwords
A common method hackers use to access accounts and steal information is brute force attacks — trying different combinations of passwords until they guess it correctly.
Passwords act as a first line of defense against unauthorized access.
If your password is “12345,” hackers won’t have any problems cracking it. A strong password makes it significantly harder for anyone to brute force their way into your account.
Educate remote workers on the importance of using strong passwords across all their accounts and devices. This will help prevent hackers from gaining access to company information.
Strong passwords have the following characteristics:
- At least eight characters (more is better)
- A mixture of uppercase and lowercase letters
- Inclusion of numbers and special characters (e.g., @#&$)
Make sure to emphasize the importance of using different passwords across all accounts.
One survey found that 39% of online users use the same passwords for different accounts. A single leak of login credentials for one account can put others at risk.
Consider using a password manager. This will make it easier for remote teams to access accounts without having to remember complex passwords.
4. Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Even strong passwords aren’t completely bullet-proof. Hackers can still access an account if a data breach reveals an employee’s username and password.
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional information like a verification code. Without this code, users can’t access an account even if they enter the correct username and password.
Using 2FA is effective at restricting unauthorized access. Sending an SMS code to a recovery phone number blocked 100% of automated bots and 76% of targeted attacks.
Having to wait for and enter a verification code may seem like a minor inconvenience, but it far outweighs the risks of cybercriminals gaining unauthorized entry to a company account.
Companies can use platforms like spores.app for different tasks. Setting up 2FA will be much easier if you have one software that does everything.
But if your company depends on many cloud-based services and collaboration tools, be sure to set up 2FA on all of them. Use software like Google Authenticator to generate verification codes.
5. Issue Work Devices
An essential part of HR management is setting up employees with the appropriate systems and bringing them up to speed. IT teams then configure devices and install antivirus software to protect against viruses.
Ensuring data security is easier to manage when employees are working in the office with work-issued devices. However, a potential threat to the company’s security occurs when remote employees use their personal devices to access work files.
While the company may follow certain security protocols, there’s no way to know if remote employees follow the same procedures with their own computers.
One way to address these concerns is to issue work devices to remote employees. Then, have your IT team configure and secure those devices before issuing them out.
Routers present another security vulnerability.
Most routers come with a default username and password. If you don’t change these credentials, hackers can log in and access sensitive information.
Have remote workers change the password for their routers. This may sound obvious, but one survey found that 18% of respondents didn’t change the administrator password on their routers.
There are other security measures that remote teams can take.
These include updating the router’s firmware and switching to Wi-Fi Protected Access II (WPA2), a security standard that encrypts data over wireless networks.
6. Create Frequent Backups
Data loss can disrupt an organization’s operations and cause huge financial losses.
No matter how many precautions you take, your company is still vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers may discover a new exploit, or an employee may make a simple mistake.
Your company must have an effective recovery system in place, which involves creating frequent backups of important files.
Cybersecurity experts recommend the “3-2-1 rule” for data backups. This rule states that you should:
- Keep at least three copies of your data. This prevents a single incident like fires or a hardware failure from destroying all your data. Make sure to keep multiple copies of your backups, whether it’s through data center infrastructures, cloud storage, hard drives, etc.
- Store backup copies in two formats. The most common way to backup data is by using an external hard drive. The problem, though, is that hardware can fail over time. Use at least two different types of storage for your backup copies.
- Keep one copy offsite. Storing backups in one location isn’t a good idea for obvious reasons. Keep at least one copy offsite, either in the cloud or another location (both would be better).
Keeping regular backups protects against valuable data loss.
Make sure to back up important information a few times a week. If you ever need to recover data, you can always restore a backup.
Conclusion
More people today are working remotely. It’s a trend that will likely continue as more companies embrace flexible work options to retain and attract talent.
The flexibility that working from home provides is certainly appealing. But it also comes with several challenges in terms of keeping networks secure.
Follow the cybersecurity practices described here to protect against cyberattacks and provide a more secure environment for remote employees.